Introduction
Introduction to three-tier architecture
The three-tier architecture is the most popular implementation of a multi-tier architecture and consists of a single presentation tier, logic tier, and data tier. The following illustration shows an example of a simple, generic three-tier application.
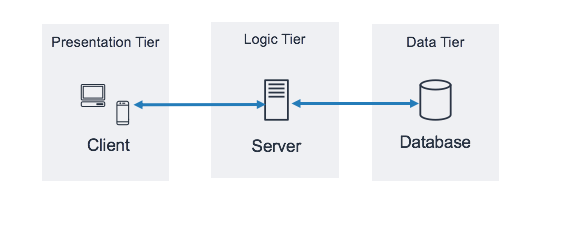
Three-tier architecture includes:
- Presentation tier / Web Tier: interface layer so users can interact directly (eg: website or mobile application UI).
- Logic tier / App tier: layer to process logic and execute user commands.
- Data tier: data storage layer of the app.
Advantages of implementing three-tier architecture:
- Modularity: this architecture helps us modularize the app into independent parts. This helps the dev team focus on developing each layer of the app, resulting in changes being applied as quickly as possible. In addition, it also helps recover the app faster after the server is down due to an error or disaster thanks to being able to localize and repair the faulty part.
- High availability: because the architecture deploys applications across multiple Availability Zones, the AZs are designed so that there is no failure that affects 2 AZs at the same time (fault isolation).
- High redundancy: AWS allows deploying a stand by or replica version of the primary database on the remaining AZ. If the main database is down, the application can still retrieve data from the replica database.